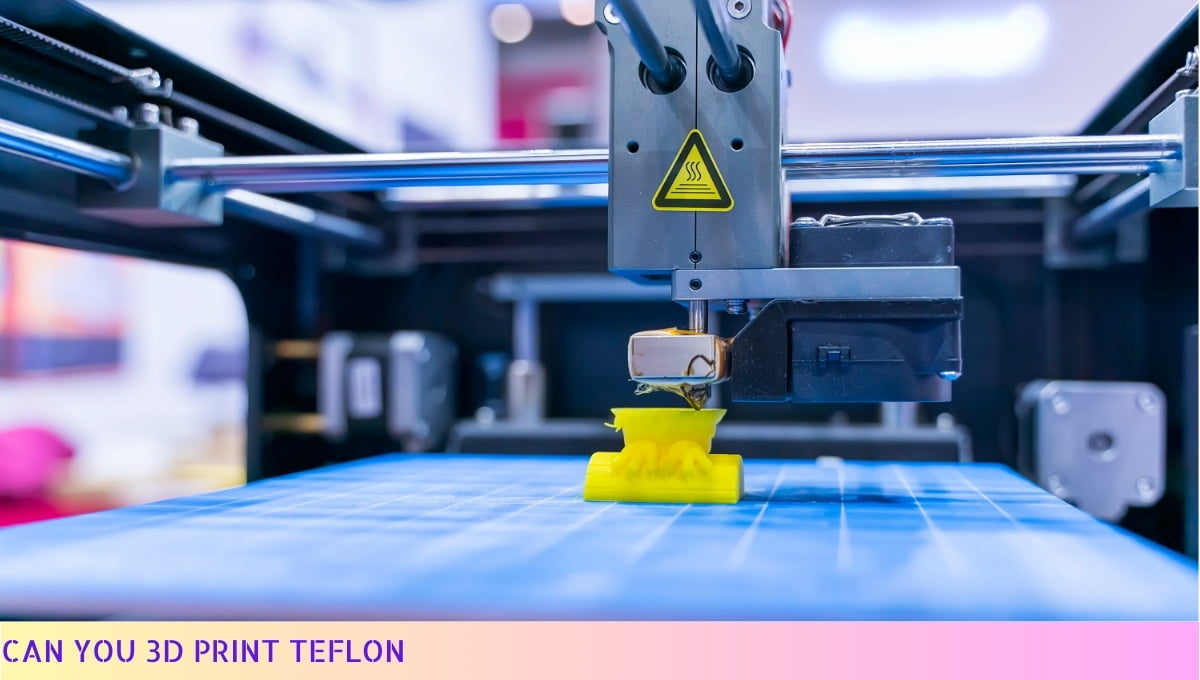
Yes, you can 3D print Teflon!
Teflon, also known as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is a high-performance polymer with excellent non-stick and heat-resistant properties.
With the advancements in 3D printing technology, it is now possible to print objects using Teflon filament. This opens up a wide range of possibilities for creating custom Teflon parts and prototypes.
However, it’s important to note that Teflon has unique printing requirements, such as a high printing temperature and specialized equipment.
So, if you’re considering 3D printing with Teflon, make sure to do your research and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for optimal results.
I. The Basics of Teflon
Let’s talk about Teflon, folks! This remarkable material has revolutionized the world of nonstick coatings and is widely used in various industries.
Now, I’m here to give you the lowdown on what makes Teflon so special and how it works its magic.
What is Teflon?
Teflon is a brand name for a type of polymer known as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). It was discovered back in the 1930s by a chemist named Roy Plunkett.
This dude accidentally stumbled upon this slippery substance while working on a refrigerant gas project. Talk about a happy accident!
Now, Teflon is known for its incredible nonstick properties. It’s like having a superpower against sticky situations. Whether it’s a frying pan, a conveyor belt, or even a printer roller, Teflon keeps things from sticking like glue.
How does Teflon work?
Well, my friends, Teflon has a unique molecular structure that sets it apart from other materials.
It’s made up of carbon and fluorine atoms arranged in a chain-like pattern. This arrangement creates a super smooth surface that nothing can cling to.
Imagine a bunch of tiny ball bearings rolling around on a surface. That’s what Teflon does to anything that tries to stick to it.
It creates a slippery barrier that repels substances like oil, water, and even glue. It’s like having a force field against adhesion!
What are the uses of Teflon?
Teflon’s nonstick properties have made it a superstar in the kitchen. You’ll find it coating your favorite frying pans, baking sheets, and even waffle makers.
No more scrubbing and scraping to remove burnt-on food! Teflon makes cleanup a breeze.
But Teflon isn’t just for the kitchen. It’s used in a wide range of industries, from automotive to aerospace.
Its low friction properties make it ideal for bearings, gears, and seals. It’s also heat resistant, so it can handle extreme temperatures without breaking a sweat.
And guess what? Teflon has even made its way into the world of 3D printing. Yep, you heard me right! Now you can print objects with Teflon, opening up a whole new realm of possibilities.
So there you have it, folks! Teflon, the superhero of nonstick coatings, has a molecular structure that repels anything that tries to stick to it.
From frying pans to 3D printed objects, Teflon is a game-changer in various industries. Now go forth and enjoy a life free from sticky situations!
II. 3D Printing Technology and Materials
Overview
When it comes to 3D printing, the technology has truly revolutionized the manufacturing industry. It allows us to create three-dimensional objects by layering materials on top of each other.
But what materials can we use for 3D printing? Well, the options are vast, my friend!
Common 3D Printing Materials
Let’s delve into some of the most commonly used materials in 3D printing:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): PLA is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane. It’s a popular choice due to its low melting point and ease of use.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): ABS is a strong and durable thermoplastic commonly used in various industries. It’s known for its impact resistance and can withstand higher temperatures than PLA.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): PETG is a versatile material that combines the strength of ABS with the ease of printing of PLA. It’s known for its durability, transparency, and resistance to chemicals.
- Nylon: Nylon is a strong and flexible material used in a wide range of applications. It’s known for its excellent mechanical properties and high resistance to impact.
Specialty 3D Printing Materials
Apart from the commonly used materials, there’s a whole world of specialty materials for 3D printing. These materials offer unique properties that cater to specific applications.
Some examples include:
- Wood Filament: This filament contains wood fibers mixed with a binding polymer, allowing you to create objects with a wooden-like appearance and texture.
- Metal Filament: By combining metal particles with a polymer binder, you can create objects that resemble metal and even exhibit some metallic properties.
- Flexible Filament: As the name suggests, this filament is highly flexible, making it suitable for creating objects that require elasticity or rubber-like properties.
Challenges and Innovations
Of course, with every technology, there are challenges to overcome. When it comes to 3D printing, one significant challenge is finding the right balance between print speed and print quality.
Faster printing may sacrifice the intricacy and accuracy of the final object.
However, researchers and innovators are constantly pushing the boundaries of 3D printing technology.
They are developing new materials with enhanced properties, such as heat resistance, electrical conductivity, and even biocompatibility for medical applications.
This continuous innovation ensures that the possibilities of 3D printing are expanding every day.
3D printing offers a wide range of materials to bring our creations to life. From the commonly used PLA and ABS to specialty materials like wood filament and metal filament, the options are endless.
As technology advances, we can expect even more exciting materials and innovations in the world of 3D printing. So, my friend, let your imagination run wild and start creating!
III. Challenges of 3D Printing Teflon
1. High Melting Point
One of the major challenges in 3D printing Teflon is its high melting point. Teflon, also known as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), has a melting point of around 327 degrees Celsius (620 degrees Fahrenheit).
This makes it difficult to melt and extrude through a 3D printer nozzle, which typically operates at lower temperatures. The high melting point requires specialized equipment and techniques to achieve successful 3D prints.
2. Low Surface Energy
Teflon is well-known for its low surface energy, which makes it highly resistant to sticking. While this property is advantageous in many applications, it poses a challenge for 3D printing.
The low surface energy makes it difficult for the layers of Teflon to adhere to each other during the printing process. This can result in weak and brittle prints that are prone to delamination or separation.
3. Limited Availability of Teflon Filaments
Unlike some other 3D printing materials, such as PLA or ABS, Teflon filaments are not as widely available in the market.
This limited availability can make it challenging for users to find suitable Teflon filaments for their 3D printing projects. Additionally, the cost of Teflon filaments can be higher compared to other materials, further limiting its accessibility.
4. Post-Processing Difficulties
Post-processing Teflon 3D prints can be a complex task. Teflon has excellent chemical resistance, which means traditional methods of smoothing or finishing, such as sanding or acetone vapor smoothing, are not effective.
Specialized techniques, such as thermal treatment or chemical etching, may be required to achieve the desired surface finish and functional properties.
5. Print Accuracy and Dimensional Stability
Due to its unique properties, Teflon can be challenging to print with high accuracy and dimensional stability. Teflon has a tendency to shrink and warp during the printing process, leading to distortions in the final print.
Achieving precise and consistent dimensions can be difficult, requiring careful calibration and optimization of printing parameters.
6. Health and Safety Considerations
While Teflon itself is generally considered safe for use in various applications, it is important to handle and process it with caution.
The high temperatures involved in 3D printing Teflon can release potentially harmful fumes, including perfluorinated compounds. Proper ventilation and protective measures should be taken to ensure a safe working environment.
IV. Potential Applications of 3D Printed Teflon
Unleashing the Power of Teflon in 3D Printing
Teflon, with its remarkable properties, opens up a world of possibilities in the realm of 3D printing. The ability to create intricate shapes and structures using this versatile material has the potential to revolutionize various industries.
Let’s explore some of the exciting applications that 3D printed Teflon can offer.
1. Aerospace and Aviation
The aerospace and aviation sectors demand materials that can withstand extreme temperatures, harsh chemicals, and provide exceptional durability.
3D printed Teflon can rise to this challenge, offering lightweight components that are resistant to corrosion and possess excellent thermal stability.
From aircraft parts to engine components, Teflon’s low friction properties can enhance performance and efficiency, making it an ideal choice for these industries.
2. Medical and Healthcare
In the medical field, precision and biocompatibility are of utmost importance. 3D printed Teflon can play a vital role in manufacturing custom medical devices, implants, and surgical instruments.
Its non-reactive nature, combined with its low friction and self-lubricating properties, make Teflon an excellent choice for applications such as prosthetics, orthopedic implants, and even drug delivery systems.
By harnessing the power of Teflon, medical professionals can provide enhanced patient care and improved treatment outcomes.
3. Electronics and Electrical Engineering
The electronics industry constantly seeks materials that can withstand high temperatures, provide electrical insulation, and offer exceptional chemical resistance.
3D-printed Teflon can meet these requirements, making it suitable for manufacturing components like circuit boards, connectors, and insulators. Its ability to maintain stability in extreme conditions makes Teflon an attractive option for industries where reliability is paramount.
4. Chemical Processing
Chemical processing plants require materials that can resist corrosive chemicals and maintain their integrity over time.
3D-printed Teflon can provide the solution, enabling the creation of complex, chemically resistant equipment such as valves, seals, and gaskets.
By leveraging Teflon’s unique properties, industries can enhance safety, increase efficiency, and reduce maintenance costs.
5. Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, hygiene and cleanliness are critical. 3D printed Teflon can be used to create food-grade equipment and containers that are non-toxic, easy to clean, and resistant to high temperatures.
From customized food molds to non-stick coatings for cooking surfaces, Teflon can contribute to improved food processing and packaging, ensuring the highest standards of safety and quality.
The advent of 3D printed Teflon presents a game-changing opportunity for various industries.
Its unique combination of properties, including low friction, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, make it a versatile material for a wide range of applications.
From aerospace and medical fields to electronics and chemical processing, the potential of 3D printed Teflon is truly exciting.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative uses for this extraordinary material. So, let’s embrace the future of 3D printing with Teflon and unlock a world of endless possibilities.
Can You 3d Print Teflon – FAQs
1. Can you 3D print Teflon?
Yes, it is possible to 3D print Teflon. However, due to its unique properties and challenges associated with its processing, it requires specialized equipment and expertise.
2. What is Teflon?
Teflon is a brand name for a type of polymer called polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). It is known for its nonstick properties, high temperature resistance, and chemical inertness.
3. What are the benefits of 3D printing Teflon?
3D printing Teflon allows for the creation of complex shapes and intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through traditional manufacturing methods. It also provides the advantage of customization and rapid prototyping.
4. What are the challenges in 3D printing Teflon?
Teflon has a high melting point and low thermal conductivity, making it challenging to melt and extrude during the 3D printing process. It also has a tendency to warp and shrink, requiring careful consideration of the printing parameters and design modifications.
5. What type of 3D printers can print Teflon?
3D printers that can handle high-temperature materials, such as those equipped with an all-metal hotend and a heated build plate, are typically required to 3D print Teflon. These printers are capable of reaching and maintaining the elevated temperatures needed for processing Teflon.
6. Is Teflon filament readily available for 3D printing?
Teflon filament is not as commonly available as other materials due to its unique characteristics and processing challenges. However, there are suppliers that offer Teflon filament specifically designed for 3D printing applications.
7. What are the applications of 3D printed Teflon?
3D printed Teflon finds applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, chemical processing, and electronics. It is used for creating parts that require excellent chemical resistance, low friction, high temperature tolerance, and electrical insulation properties.
8. Are there any safety considerations when 3D printing Teflon?
Yes, safety precautions should be taken when 3D printing Teflon as it can release toxic fumes when heated above its melting point. Adequate ventilation and the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) are recommended.
9. Can Teflon parts be post-processed after 3D printing?
Teflon parts can be post-processed through techniques such as machining, sanding, or polishing to achieve the desired surface finish or dimensional accuracy. However, it is important to ensure that the post-processing methods do not compromise the unique properties of Teflon.
10. Can Teflon be combined with other materials in 3D printing?
Yes, Teflon can be combined with other materials in 3D printing to create hybrid structures with enhanced properties. For example, it can be blended with other polymers or reinforced with additives to improve strength, flexibility, or conductivity.
Wrapping Up
So, can you 3D print Teflon? The answer is a resounding no. Teflon, also known as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is a high-performance polymer with unique properties.
Its extremely high melting point and low coefficient of friction make it nearly impossible to 3D print using traditional methods.
However, there are alternative materials, such as PTFE-filled filaments, that mimic some of Teflon’s characteristics and can be used for 3D printing.
So, while you can’t directly 3D print Teflon, there are options available if you’re looking for similar properties in your prints.